Generation of Bacterial Artificial Chromosome (BAC) transgenes
BAC trangenes are a rather novel tool in the toolbox for transgenesis in mammals. The advantage of BAC transgenes lies in the fact that in most cases all promoter elements are present without their prior characterisation. Also, BAC transgenes integrate with lower copy numbers and are less position-dependent than conventional transgenes. In comparison to targeted insertion by homologous recombination in ES cells the generation of a BAC transgene is easy and fast. They also do not lead to a knockout allele of the respective gene.
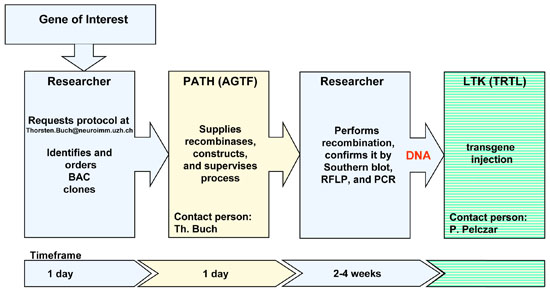
The AGTF does not yet offer the generation of BAC transgenes as full service but supports researchers in the planning and generation of BAC transgenes on many levels. During the Mouse Makers Club we discuss the strategies and different options in making such mice. We have generated a protocol which by now has been used by a number of researchers in Zurich (for the protocol: e-mail to Thorsten.Buch@neuroimm.uzh.ch). Also, we supply the respective plasmids and bacteria for the recombination process (Copeland and E/T cloning). Our collection of integration cassettes allows the easy generation of different BAC transgenes (see list below). Once you have purified your BAC transgene it will be injected by the TRT lab (Pawel Pelczar pawel.pelczar@ltk.uzh.ch (044-255-37 37)).
| Construct | Function |
|---|---|
| Cre frt Kan(R) frt | Cre expression |
| iCre frt Kan(R) frt | Cre expression |
| CreERt2 frt Kan(R) frt | tamoxifen-inducible Cre |
| tdTomato frt Kan(R) frt | strong red fluorescent color |
| dsRED-Mst frt Kan(R) frt | red fluorescent color at plasma membrane |
| Mst-tdTomato frt Kan(R) frt | strong red fluorescent color at the plasma membrane |
| lacZ frt Kan(R) frt | b-Gal expression, histological staining of cells with X-Gal |
| tdTomato-pest 2A Cre frt Kan(R) frt | short half life red color + Cre |
| CreDo and CreAc frt Kan(R) frt | Cre expression in dual marker populations |
| loxP STOP Kan(R) loxP-DTR | Cre inducible DTR expression (dual marker) |
| loxP STOP Kan(R) loxP | inducible gene expression |
| ChR2-mCherry frt Kan(R) frt | Light-inducible cation channel |